Introduction
Brugada Syndrome is a rare but potentially fatal genetic heart disorder that affects the electrical activity of the heart. It can lead to dangerous arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), which may cause sudden cardiac arrest, particularly in young and otherwise healthy individuals. Since its discovery in 1992 by Spanish cardiologists Pedro and Josep Brugada, researchers have continued to explore its genetic basis, risk factors, and treatment options.
Latest Research and Genetic Insights
Recent studies have identified additional genetic mutations beyond SCN5A that may contribute to Brugada Syndrome, including genes involved in calcium and potassium channels. Advances in genetic testing now allow for better risk assessment, especially for family members of affected individuals. Researchers are also investigating how lifestyle factors and environmental triggers influence arrhythmia development in Brugada patients.
Patient Experiences and Early Warning Signs
For many individuals, Brugada Syndrome remains asymptomatic until a major cardiac event occurs. However, some patients report warning signs such as:
Fainting episodes (syncope), often occurring during sleep
Unexplained seizures
Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeats
Family history of sudden cardiac death
These symptoms, especially when coupled with abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG) results, warrant immediate medical attention.
Advances in Diagnosis
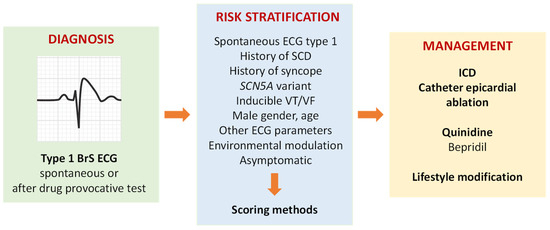
While an ECG remains the primary diagnostic tool for Brugada Syndrome, researchers have developed advanced imaging techniques and electrophysiological studies to detect hidden cases. Some hospitals now offer risk stratification tests to identify patients at the highest risk of sudden cardiac arrest, enabling more personalized treatment plans.
Evolving Treatment Approaches
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD): Still the gold standard for high-risk patients, an ICD provides life-saving intervention by detecting and correcting dangerous heart rhythms.
Medications: Anti-arrhythmic drugs like quinidine have shown promise in reducing arrhythmic episodes, particularly for those who are not ICD candidates.
Ablation Therapy: Recent advancements in catheter ablation techniques have provided an alternative for some patients, targeting the abnormal heart tissue responsible for arrhythmias.
Wearable Technology: Smartwatches and ECG-enabled devices are being explored as early warning systems for detecting heart rhythm abnormalities in Brugada patients.
Prognosis and Future Outlook
With better diagnostic tools, genetic screening, and evolving treatment strategies, the outlook for Brugada Syndrome patients continues to improve. Ongoing clinical trials are testing new drugs and gene therapies aimed at correcting the underlying electrical disturbances of the heart. Increased awareness and early intervention remain key to reducing sudden cardiac deaths associated with the syndrome.
Conclusion
Brugada Syndrome remains a challenging but increasingly manageable condition. With the latest research advancements, improved diagnostic methods, and innovative treatments, patients diagnosed with Brugada Syndrome now have more options than ever. Continued research and patient advocacy will play a crucial role in further understanding and combating this life-threatening disorder.